Cybersecurity Risk Management: A Guide to National Cybersecurity Strategy

National cybersecurity protects a country’s digital assets from cyberattacks. Cybercriminals may threaten national security and economic stability. Hence, there is a need for strict adherence to cybersecurity frameworks.
Outline:
- Guide to Developing a National Cybersecurity Strategy
- National Cyber Defense Strategies and International Best Practices
- NCS Guide: Understanding National Cybersecurity Frameworks
- NCS Cybersecurity: Strengthening National Security Against Cyber Threats
Guide to Developing a National Cybersecurity Strategy

1. Why Every Country Needs a Solid Cybersecurity Strategy
A country’s cybersecurity strategy requires adapting to the National Cyber Security Policies (NCSPs) which:
- Shield businesses from ransomware and supply chain attacks.
- Protect critical infrastructure such as healthcare, security, transport, and energy.
- Ensure compliance with cybersecurity frameworks.
- Enhance public safety with IoT advancements.
2. Essential Pillars of National Cybersecurity
The three integral pillars of a high-performing cybersecurity strategy consist of risk assessment, threat intelligence, and policy enforcement:
Risk Assessment
A full strategic risk assessment plan rotates through:
- Critical asset identification: these may include power grids, financial institutions, immigration data e.t.c
- Scanning for potential threats: In response to incidents, there is a need to stay on the radar for similar threats
- Vulnerability assessment: security teams should embrace real-time monitoring and response
- Threat Mitigation: cybersecurity awareness should focus on multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access, sensitive data encryption, and network segmentation to separate devices
Threat Intelligence
Cyber Threat Intelligence program can generate real-time insights that can prevent cyber attackers through:
- Deploying Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) for real-time cyber threat analysis
- Partnering with organizations such as the Interpol Cybercrime Directorate and Cyber Threat Alliance (CTA)
- Leveraging AI-based cybersecurity tools to detect anomalies beforehand
- Utilizing open-source threat Intelligence reports that warn organizations about emerging security threats
Policy Enforcement
The following practices can help countries remain compliant with international security laws. Hence, preventing heavy fines and minimizing exposure to cyber-attacks.
- Governments must embrace cybersecurity laws to ensure that they: protect data (GDPR), outline risk management guidelines (NIST- CSF), facilitate secure transactions (PCI – DSS), and uphold global standards in security information management (ISO 27001)
- Periodic impromptu assessments can be conducted to ensure that the organization follows cybersecurity best practices
- Through collaboration, governments can establish National Incident Response Teams – to promptly respond to cyberattack
- To forge against ever-evolving cyber-attacks, cybersecurity campaigns should be geared towards the general public, government employees, and private sector workers
National Cyber Defense Strategies and International Best Practices

1. Global Cybersecurity Implementation
Sprinklr, a leader in AI-driven customer experience solutions, highlights the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in automating cybersecurity responses, and therefore, countries have developed unique defenses to protect their key infrastructure. For example:
- In the U.S., the CISA Framework, has been automated for real-time threat intelligence and strengthening public-private unions.
- The EU has developed systems that ensure member states’ compliance with GDPR to highlight privacy and network security.
- In the U.K., National Cyber Strategy 2022, prioritizes AI-powered threat detection and automation to identify and respond to cyber threats proactively.
2. Best Practices for Cybersecurity Collaboration
Effective national cybersecurity depends on teamwork:
- Organizations such as the Interpol Cybercrime Directorate and Kaspersky aim to ensure that intelligence is effectively shared to help improve cyber incident response plans.
- Governments should enhance Computer Emergency Response Teams (CERTs) with the necessary resources to combat threats in real-time.
- Every country is mandated to enforce regulations (e.g., GDPR, NIST CSF), with their widespread AI-driven security solutions.
NCS Guide: Understanding National Cybersecurity Frameworks
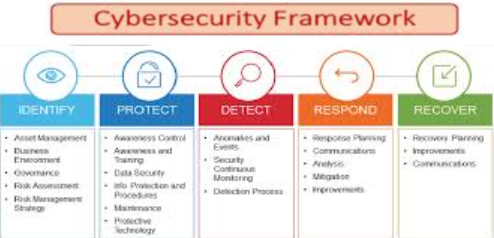
1. Why National Cybersecurity Strategy (NCS)?
An NCS protects critical assets from cyber threats via:
- Risk management and policy enforcement.
- AI-driven threat detection and automation.
- Creating awareness through cybersecurity campaigns.
2. Strengthening Cybersecurity with Security Laws
NI Cyber Security Center emphasizes strict compliance with cybersecurity policies. This helps the government to have an efficient oversight. Key frameworks include:
- NIST CSF: Standardizes cybersecurity practices globally.
- CIS Controls: Provides a prioritized list of security measures.
- Zero Trust Security Model: Ensures continuous authentication for system access.
3. Steps to Create a Resilient Cybersecurity Policy:
- Identify vulnerabilities in critical sectors.
- Align security measures with international frameworks.
- Use Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs).
- Conduct regular security audits.
NCS Cybersecurity: Strengthening National Security Against Cyber Threats

1. Why NCS Cybersecurity is Critical
Unplanned cybersecurity measures, may expose national infrastructure to:
- Ransomware that targets financial institutions.
- Phishing that may potentially compromise government communications.
- Cyber espionage which may infiltrate sensitive systems.
2. The Role of Governments and Private Sectors:
- Governments enforce regulatory frameworks (e.g., GDPR, PCI DSS).
- Private cybersecurity firms provide AI-driven solutions to detect and mitigate cyber threats.
- Public awareness programs educate citizens on secure online practices.
It is worth noting that national policies should address concerns on Social Media Security – AI- AI-generated pop-ups such as “best time to post on Instagram today” or “Twitter advanced search” are nowadays used for phishing and malware attacks.
3. Emerging Cyber Threats and How Nations Can Mitigate Them
Cyber threats evolve rapidly, making it crucial to adopt proactive security measures:
- Deepfake technology is being weaponized for misinformation.
- AI-driven phishing attacks are increasing in sophistication.
- Cryptojacking malware exploits national computing resources.
A strong National Cybersecurity Strategy must be adaptive, intelligence-driven, and collaborative. By utilizing global cybersecurity frameworks, embracing AI-powered security, and enhancing international cooperation, nations can effectively mitigate threats and safeguard digital assets.
